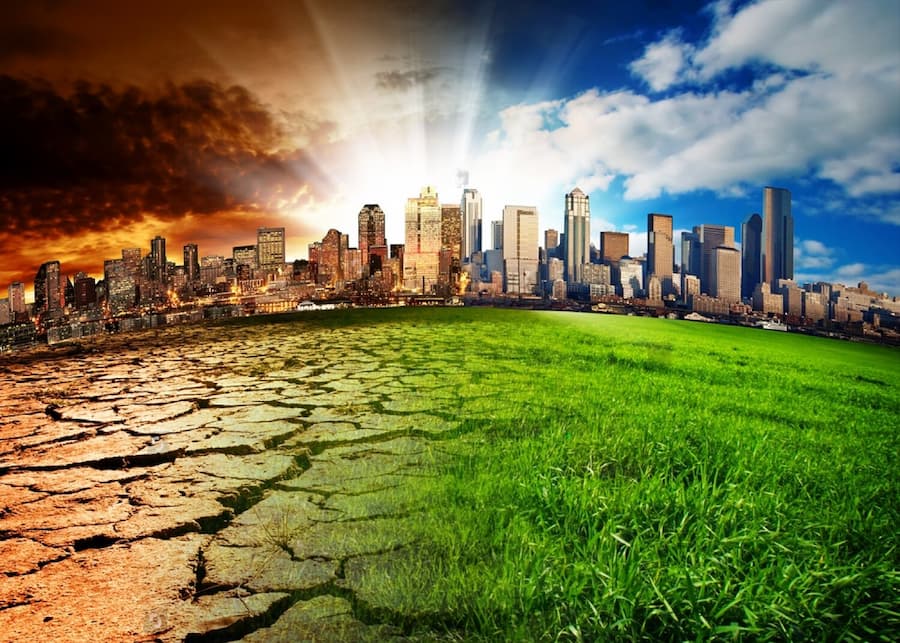

The Africa Climate Summit 2023 will take place in Nairobi Kenya from the 4th to 6th September 2023.The theme of the summit is Driving Green Growth & Climate Finance Solutions for Africa and the World.
The summit is part of concerted efforts to take action and deal with the adverse effects of climate change. Climate change threatens the basic human rights of individuals and communities around the world by violating an array of human rights such as the right to life, health, food, water, and shelter.
As a country we will be keenly following to see whether we are on course to meet our carbon budgets and progress made in reducing greenhouse gas emissions against our annual carbon targets.
Throughout the summit you will hear certain terminologies being used. But before we delve into the terminologies it is best to understand some of the principles that that underpin the protection of the environment and climate action.
What is the relationship between environmental principles and climate change. Several aspects of the environment such as waste management, air pollution, water, deforestation and biodiversity are related to climate change.
Actions taken towards protecting the environment have a huge bearing on efforts to tackle climate change. Environmental laws and policies play a critical role in assisting countries to achieve net zero greenhouse gas emissions.
Now that we have laid a basis for the relationship between environmental law principles and climate change action, let’s look at the environmental principles. Our legal framework both national and international provide for five overarching environmental principles relevant to climate change as follows:
The precautionary principle: In case of uncertainty about the risk of environmental harm, this principle allows protective measures to be taken without having to wait until the harm materializes. This principle is valuable in managing risk where there is uncertainty about the environmental impact of an issue thus serves as a risk management tool.
The prevention principle: This principle requires preventive measures be taken to anticipate and avoid environmental damage before it happens and forms the bedrock of policy and legislation on environment and climate change action.
The rectification at source principle: This principle prioritizes redress for environmental damage and ensures that damage or pollution is dealt with where it occurs. A clear path of action must be followed by governments and elected officials to intervene and establish the relationship between the full cause and effect of an activity on the ecosystem.
The polluter pays principle: The person who causes pollution should bear the costs of the damage caused and any remedy required. A key principle in environmental management, serving both as a deterrent and accountability measure for harm.
The integration principle: This principle bestows responsibility and requires that environmental protection is integrated into all other policy areas, in line with promoting sustainable development. That is to say all government departments have responsibilities to protect our environment.
Decision-makers are called upon to factor these principles into their work when taking decisions on environment and climate change relates actions.
Are there only five environmental principles? What about the no-harm principle touted as a cornerstone of international environmental law? Join us in our next article as we discuss the politics behind the no- harm principles as it relates to climate change governance.
 April 26, 2024
Shared Responsibility: Disaster Management Between Kenya's National and County Governments
April 26, 2024
Shared Responsibility: Disaster Management Between Kenya's National and County Governments
 April 17, 2024
Guarding Justice: Hire Not Persons masquerading as Lawyers
April 17, 2024
Guarding Justice: Hire Not Persons masquerading as Lawyers
 March 25, 2024
Hatua za kushtaki mtu kwa uhalifu
March 25, 2024
Hatua za kushtaki mtu kwa uhalifu
 March 25, 2024
The stages of criminal prosecution
March 25, 2024
The stages of criminal prosecution
 March 18, 2024
A Green Judiciary! Kenya does it.
March 18, 2024
A Green Judiciary! Kenya does it.